Lecture 1 What Are Information Systems?
In This Lecture You Will Learn:
- The Elements of an IS
- The Role of Computer
- System Transformation
- General System Theory
- Characteristics of Systems
- Systems of the Real World
The Elements of an IS
Every IS has:
- A human activity that needs information
- An input method for entering data
- Some process that turns the data into information
- Some stored data
- An output method for representing information
The Role of the Computer
- Computers carry out tasks also done by people and by other technologies
- Storage: signalman’s memory / hard disk
- Display: battle of Britain map / PC screen
- Calculation: mental arithmetic / program
- Communication: telephone line / LAN
- Typical advantages of computers:
- high speed, low cost, reliability,etc
- Wider questions that computer held for commercial activities.
- How do we establish the business requirements for a new system?
- What effect will the new system have on the organization?
- How do we ensure that the system we build will meet its requirements?
System Transformation
- All useful systems transform their inputs into useful outputs
- For IS, both inputs and outputs are typically information
- This transformation is the whole reason for building and operating the system
Transformation Example
- McGregor’s Delivery Scheduling System may have inputs:
- Information about orders, available stock, customer addresses, vehicle capacities…
- —and may have outputs:
- Which orders to load on each vehicle, what route the vehicle should follow…
- How does this benefit McGregor?
General Systems Theory
- System
- a very specific term
- it is more than just computer system e.g. legal system, the system of parliamentary democracy, a reservation system, etc.
- A system is rather more than just anything that shows a degree of organization.
Characteristics of Systems
- Exists in an environment – situation
- Separated from its environment by some kind of boundary.
- Inputs and outputs – from & to different environment.
- Interfaces – allows communication between user & the system.
- IS are like any other kind of system
- Every system has:
- Inputs and outputs
- A purpose (related to transformation)
- A boundary and an environment
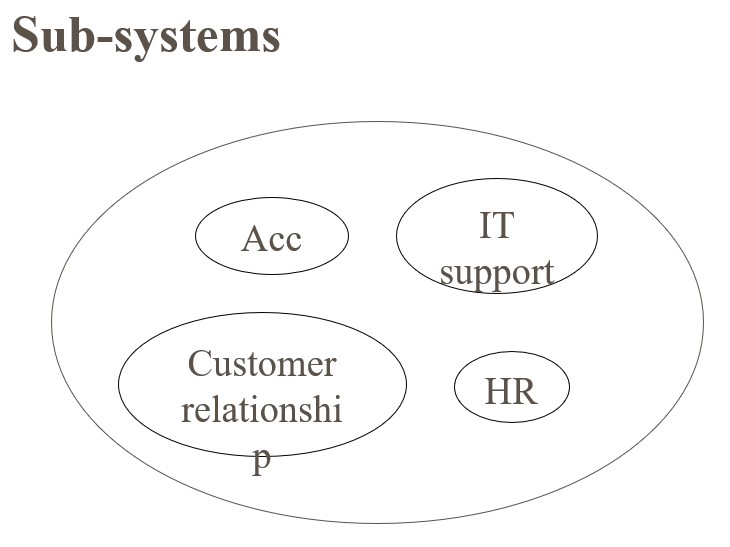
- Sub-systems and interfaces
- Control using feedback and feed-forward
- Some emergent property
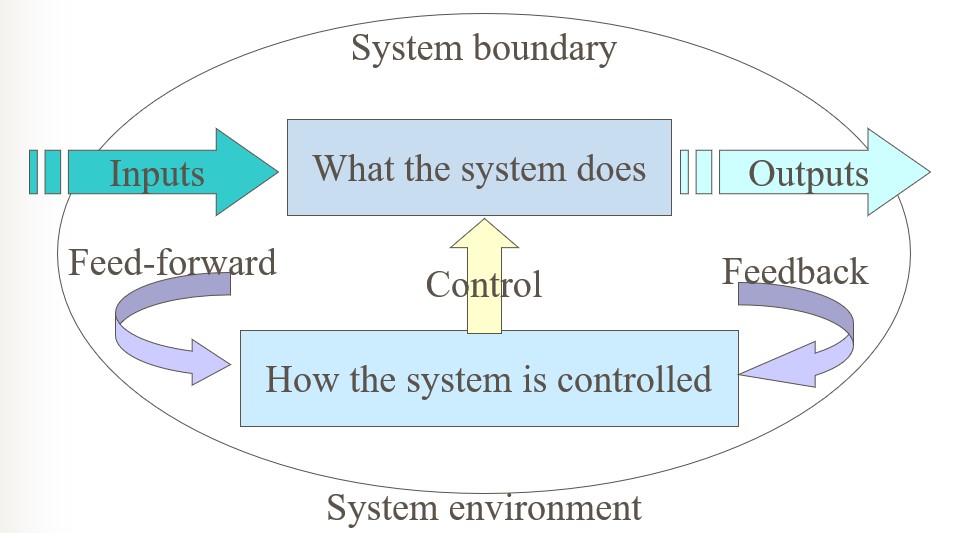
Parts of a system, and their relationship to each other.
- Boundary and environment
- Two systems may be closely related, may have identical boundary, but yet still distinct.
- Inputs and outputs
- Purpose of system is to transform input into output, this is how they fulfill their objectives.
Input and outputs
| System | Inputs | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| A student | Information, exercise, guidance | New knowledge, new ideas, solutions |
| A family | Money, purchases, daily news | New citizen, product of family member’s work |
| A business | Raw material and labor, investment, customer order | Finished products, profits and taxes, company report |
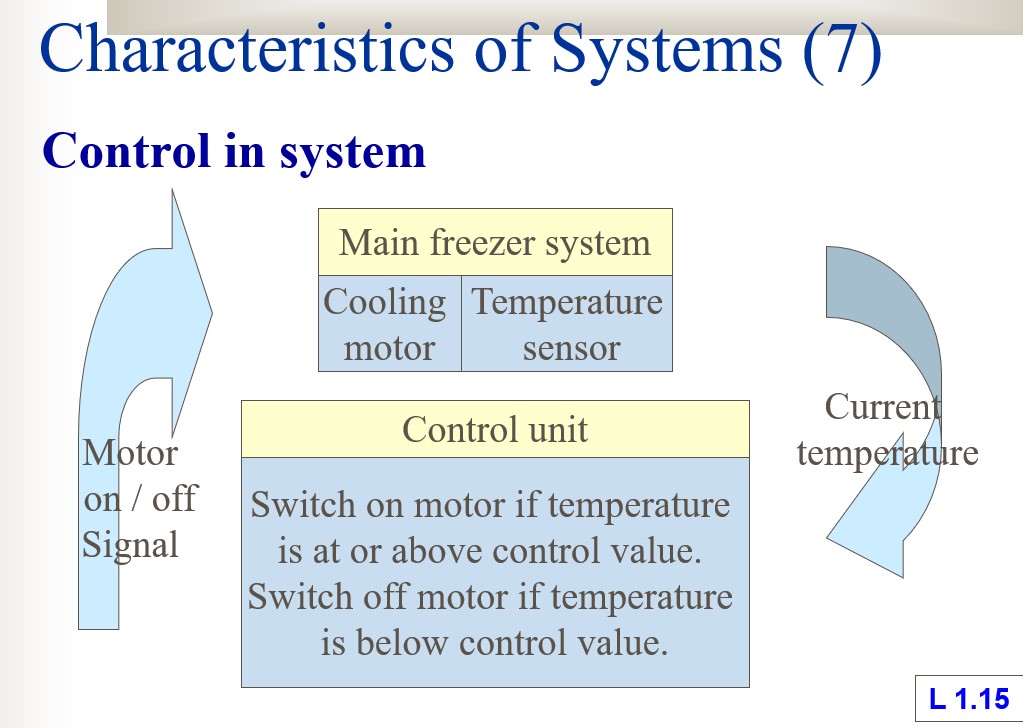
Feedback
- One or more output of the system is sampled and feed back to the control unit.
- For example, a sensor samples the temperature in the main freezer compartment and this is feed back to the control unit.
Feed-forward
- It relies on sampling system’s inputs rather than outputs.
- For example, the Christmas toy business
Emergent properties
- The system possesses some feature or ability of its own that is not present in any of its components. e.g. components of a car.
Holistic concept
- Thinking about each system as a whole.
Systems of interest in this subject
- System can be natural or artificial.
- Human activity system.
| System | Purpose of system | Different perspective |
|---|
- This subject is more concern with artificial kind of system.
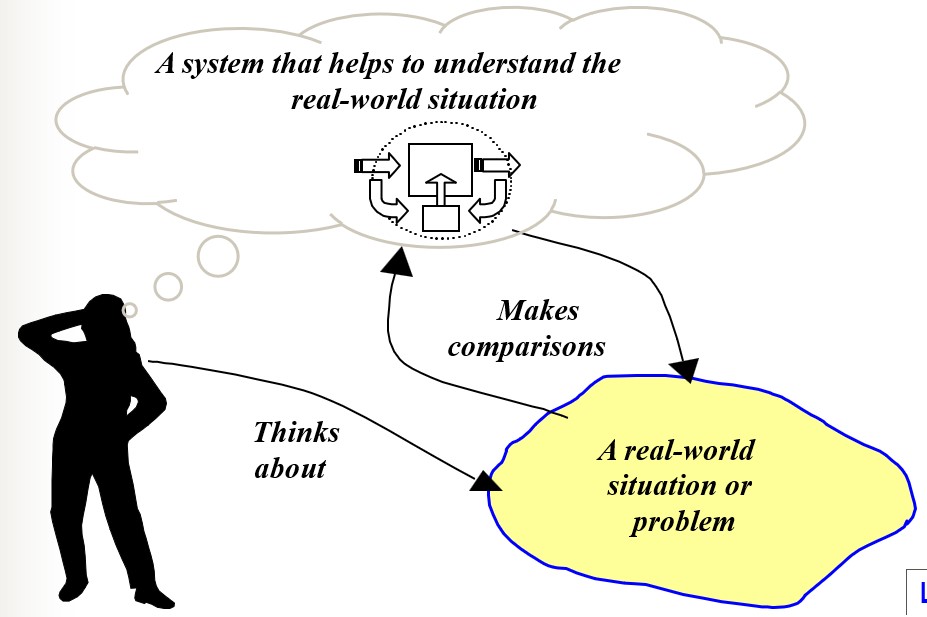
Are Systems Real?
Maybe, maybe not!
- Systems thinking is useful because it helps to analyse and understand problems
- What matters are the understanding you achieve
- You can choose to see anything as a system, whether or not it really is one
Systems and the Real World
Summary
In this lecture you have learned about:
- What are the elements of an IS?
- The role of computer
- The process of system transformation
- The general system theory
- The characteristics of systems
- The relation between system and the real world