Chapter 8: Security
The Security Problem
- The Security Problem
- Program Threats
- System and Network Threats
- Cryptography as a Security Tool
- User Authentication
- Implementing Security Defenses
- Firewalling to Protect Systems and Networks
- Computer-Security Classifications
- An Example: Windows XP
Objectives
- To discuss security threats and attacks
- To explain the fundamentals of encryption, authentication, and hashing
- To examine the uses of cryptography in computing
- To describe the various countermeasures to security attacks
The Security Problem
- Security must consider external environment of the system, and protect the system resources
- Intruders (crackers) attempt to breach security
- Threat is potential security violation
- Attack is attempt to breach security
- Attack can be accidental or malicious
- Easier to protect against accidental than malicious misuse
Security Violations
- Categories
- Breach of confidentiality
- Breach of integrity
- Breach of availability
- Theft of service
- Denial of service
- Methods
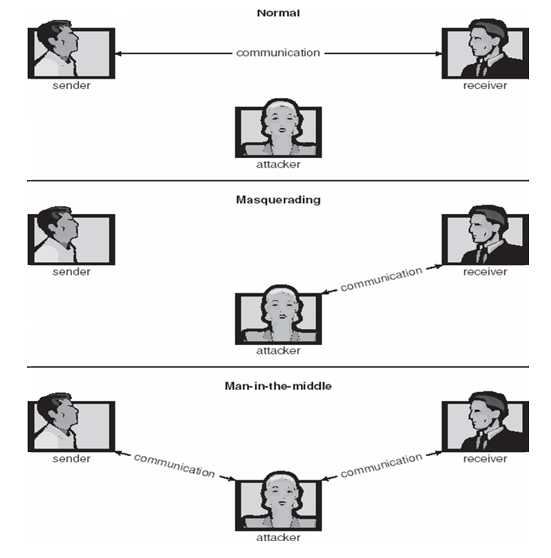
- Masquerading (breach authentication)
- Replay attack
- Message modification
- Man-in-the-middle attack
- Session hijacking
Standard Security Attacks
Security Measure Levels
- Security must occur at four levels to be effective:
- Physical
- Human
- Avoid social engineering, phishing, dumpster diving
- Operating System
- Network
- Security is as weak as the weakest link in the chain
Program Threats
- Trojan Horse
- Code segment that misuses its environment
- Exploits mechanisms for allowing programs written by users to be executed by other users
- Spyware, pop-up browser windows, covert channels
- Trap Door
- Specific user identifier or password that circumvents normal security procedures
- Could be included in a compiler
- Logic Bomb
- Program that initiates a security incident under certain circumstances
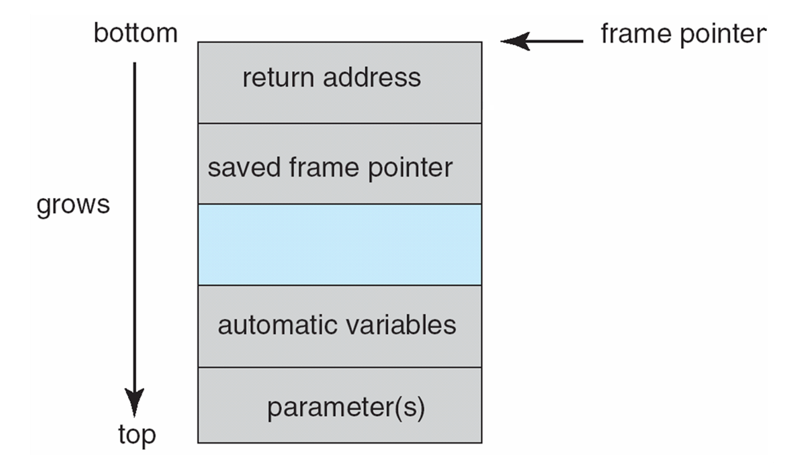
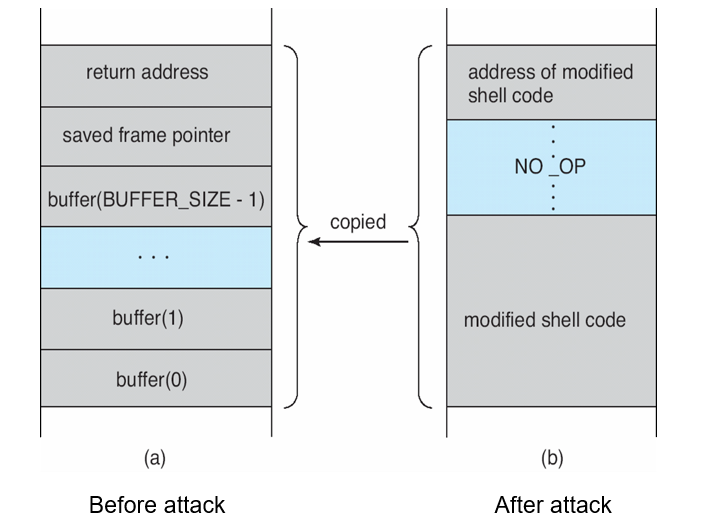
- Stack and Buffer Overflow
- Exploits a bug in a program (overflow either the stack or memory buffers)
C Program with Buffer-overflow Condition
#include <stdio.h>
#define BUFFER SIZE 256
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buffer[BUFFER SIZE];
if (argc < 2)
return -1;
else {
strcpy(buffer,argv[1]);
return 0;
}
}
Layout of Typical Stack Frame
Modified Shell Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
execvp(‘‘\bin\sh’’,‘‘\bin \sh’’, NULL);
return 0;
}
Hypothetical Stack Frame
Program Threats (Cont.)
- Many categories of viruses, literally many thousands of viruses
- File
- Boot
- Macro
- Source code
- Polymorphic
- Encrypted
- Stealth
- Tunneling
- Multipartite
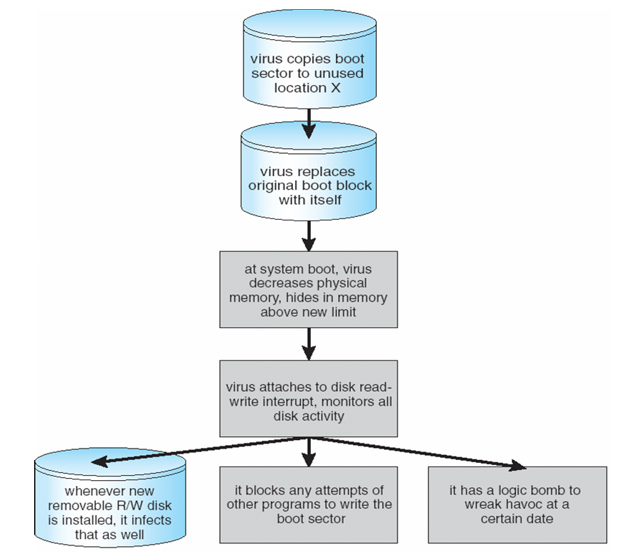
A Boot-sector Computer Virus
System and Network Threats
- Worms – use spawn mechanism; standalone program
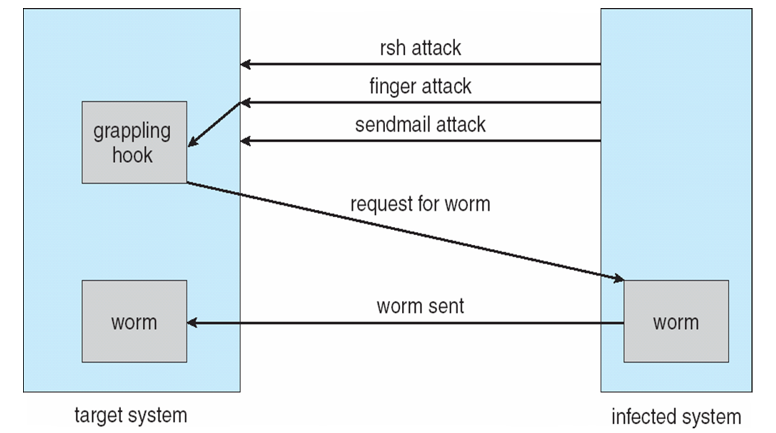
- Internet worm
- Exploited UNIX networking features (remote access) and bugs in finger and sendmail programs
- Grappling hook program uploaded main worm program
- Port scanning
- Automated attempt to connect to a range of ports on one or a range of IP addresses
- Denial of Service
- Overload the targeted computer preventing it from doing any useful work
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDOS) come from multiple sites at once
finger is a program you can use to find information about computer users
The Morris Internet Worm