What is Business Intelligence?
According to vendors:
- a segment of information technology that comprises software systems that enable finding, storing, organising and supplying data; when incorporated into an information system, it enables company to utilise real-time analysis of information
- a category of applications and technologies for gathering, storing, analysing, reporting on and providing access to data to help enterprise users make better business decisions
- Business intelligence (BI) is an umbrella term that includes the applications, infrastructure and tools, and best practices that enable access to and analysis of information to improve and optimize decisions and performance.
Gartner is the world’s leading information technology research and advisory company.
“We deliver the technology-related insight necessary for our clients to make the right decisions, every day
- In the 1970s, there were decision support systems (DSS)
- In the 1980s, there were EIS, OLAP, GIS, and more
- Data warehousing and dashboards/scorecards became popular in the 1990s
- Howard Dresner, a Gartner analyst, coined the BI term in the early 1990s
- Today there is much discussion of analytics
- There are many BI definitions, but the following is useful
Businesses Need Support for Decision Making
- Uncertain economics
- Rapidly changing environments
- Global competition
- Demanding customers
- Taking advantage of information acquired by companies is a Critical Success Factor.
The Information Gap
- The shortfall between gathering information and using it for decision making.
- Firms have inadequate data warehouses.
- Business Analysts spend 2 days a week gathering and formatting data, instead of performing analysis. (Data Warehousing Institute).
- Business Intelligence (BI) seeks to bridge the information gap.
BI
- Tools and techniques to turn data into meaningful information.
- Process: Methods used by the organization to turn data into knowledge.
- Product: Information that allows businesses to make decisions
BI Applications
- Customer Analytics
- Human Capital Productivity Analysis
- Business Productivity Analytics
- Sales Channel Analytics
- Supply Chain Analytics
- Behavior Analytics
What is Business Intelligence?
- Collecting and refining information from many sources (internal and external)
- Analyzing and presenting the information in useful ways (dashboards, visualizations)
- So that people can make better decisions
- That help build and retain competitive advantage.
Decision Making Process
- Managers usually make decisions by following a four-step process
- Define the problem (or opportunity)
- Construct a model that describes the real- world problem
- Identify possible solutions to the modeled problem and evaluate the solutions
- Compare, choose, and recommend a potential solution to the problem
Simon’s Model of Problem Solving
- Decision-making consists of three major phases—intelligence, design, and choice [Simon]
- H.A. Simon. 1960. The New Science of Management Decision. Harper and Row, NY.
- Newell, A., & Simon, H.A. (1972). Human Problem Solving. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- Intelligence which deals with the problem identification and the data collection on the problem.
- Design which deals with the generation of alternative solutions to the problem at hand.
- Choice which is selecting the ‘best’ solution from amongst the alternative solutions using some criterion.
Example
A farmer with his wolf, goat, and cabbage come to the edge of a river they wish to cross. There is a boat at the river’s edge, but of course, only the farmer can row. The boat can only handle one animal/item in addition to the farmer. If the wolf is ever left alone with the goat, the wolf will eat the goat. If the goat is left alone with the cabbage, the goat will eat the cabbage. What should the farmer do to get across the river with all his possessions?
Phase I: Intelligence
- Problem Identification and Definition
- What’s the problem?
- Why is it a problem?
- Whose problem is it?
Phase II: Design
- Problem Structuring
- Generate alternatives
- Set criteria and objectives
- Develop models and scenarios to evaluate alternatives
- Solve models to evaluate alternatives
- A lot of creativity and innovation is required to design solutions.
Phase III: Choice
- Solution
- Determine the outcome of chosen alternatives
- possible solutions are compared against one another to find out the most suitable solution.
- Select the/an outcome consistent with the decision strategy
- Determine the outcome of chosen alternatives
Definitions of Business Intelligence
- “The process of taking large amounts of data, analyzing that data and presenting a high level set of reports that condense the essence of that data into the basis of business actions, enabling management to make fundamental daily business decisions ” (Stackowiak et al 2007).
- “The way and method of improving business performance by providing powerful assists for executive decision maker to enable them to have actionable information at hand.” ( Cui et al-2007).
What is BI?
- Business intelligence (BI) is a set of theories, methodologies, architectures, and technologies that transform raw data into meaningful and useful information for business purposes.
4 Types of Actionable Information
- Actionable information is meaningful data that is useful to making a decision or solving a problem.
- Timely
- Information that applies to now or the near future. Such as a weather report for tomorrow.
- Accurate & Precise
- Information that is accurate and precise. For example, a weather report that describes the weather by hour for the next 48 hours with a reasonably high probability of being correct.
- Credible
- Information that comes from credible sources such as a national weather agency.
- Relevant
- The relevance of information to a decision or problem.
Analytical technologies
- 3 Major Categories:
- Descriptive analytics provide insight into the past and answer: “What has happened?”
- Descriptive analytics are useful because they allow us to learn from past behaviors, and understand how they might influence future outcomes.
- Descriptive statistics are useful to show things like, total stock in inventory, average dollars spent per customer
- Common examples of descriptive analytics are reports that provide historical insights regarding the company’s production, financials, operations, sales, finance, inventory and customers.
Analytical technologies
- Predictive analytics - Understanding the future, the ability to “Predict” what might happen
- Predictive analytics can be used throughout the organization, from forecasting customer behavior.
- Prescriptive analytics - Advise on possible outcomes
- prescriptive analytics predicts not only what will happen, but also why it will happen providing recommendations.
- Optimization is used to examine how you can achieve the best outcome for a particular situation
BI Architecture
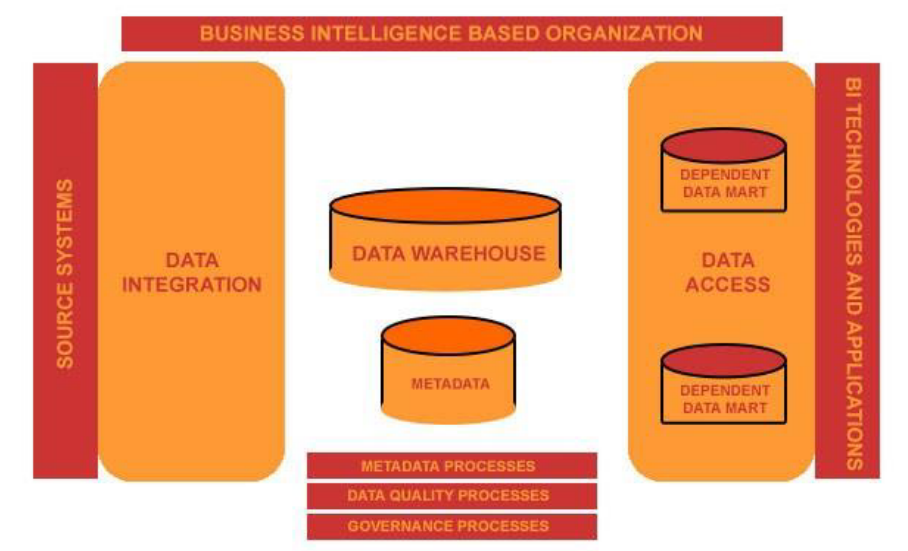
Things are getting more complex
- Source systems include social media, machine sensing, and click stream data (Big Data)
- The cloud, Hadoop/Reduce, and appliances are being used as data stores
- Advanced analytics are growing in popularity and importance
BI Components and Architecture
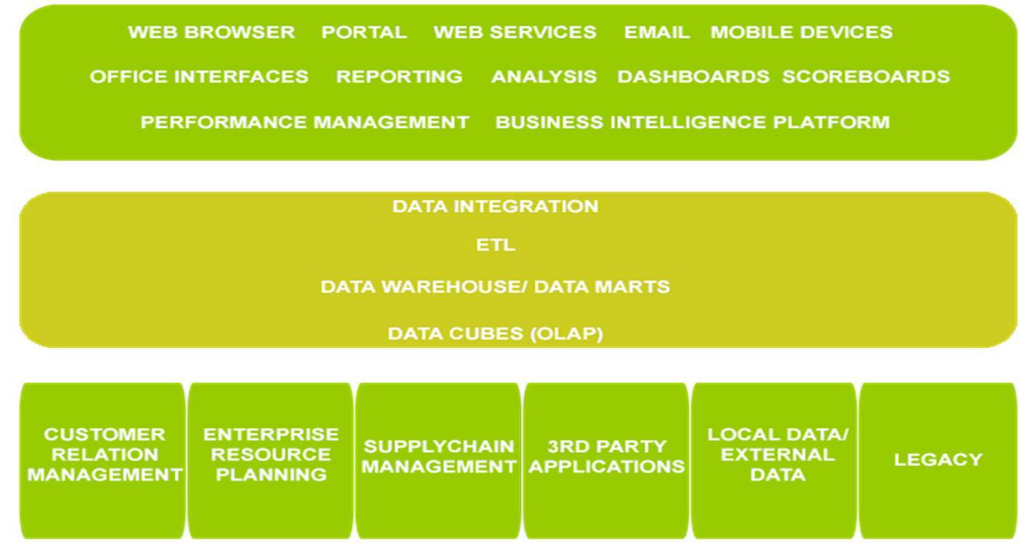
Data Warehouse
The data warehouse:
- must make an organization’s information easily accessible
- must present the organization’s information consistently
- must be adaptive and resilient to change
- must be a secure support that protects our information assets
- must serve as the foundation for improved decision making
- the business community must accept the data warehouse if it is to be deemed successful
Business and Decision Making Process
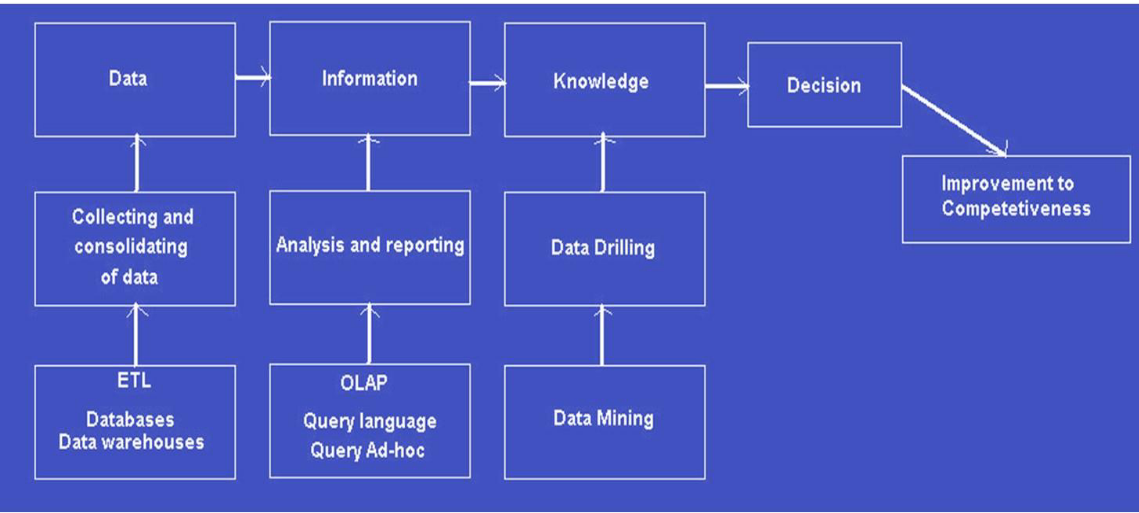
Functional areas of BI Tool
- ETL tools - ETL tools and processes are responsible for the extraction of data from one or many source systems, as they transform data from many different formats into a common format and then load that data into a data warehouse. (Schink, 2009).
- Data warehouse - A data warehouse is a collection of relevant business data that is organized and validated (Cody et al – 2002) so that it can be analyzed to support business decision making.
- Data warehouse are populated with data that has been extracted from distributed databases, often heterogeneous and in some cases, external to the organization which is using it.
- Query tools and reporting - A querying and reporting tool helps to run regular reports, create organized listings and perform cross tabular reporting and querying. The query and reporting tools are meant to allow the users to interact directly with the organization’s data.
Data Staging Area - ETL
- EXTRACTION
- reading and understanding the source data and copying the data needed for the data warehouse into the staging area for further manipulation.
- TRANSFORMATION
- cleansing, combining data from multiple sources, deduplicating data, and assigning warehouse keys
- LOADING
- loading the data into the data warehouse presentation area
Functional areas of BI Tool
- OLAP Techniques - The OLAP attempts to analyze complex data in real time on a database that is constantly updated with transactional data. The OLAP optimizes the searching of huge data files by means of automatic generation of SQL queries. OLAP enables managers to analyze data from multiple perspectives and explore it in order to discover hidden information.
- Data Mining - The data mining process involves discovering various patterns, generalizations, regularities and rules in data sources. Knowledge from data mining may be used to predict an outcome of a decision and can also describe reality.
Summary
- Vendors define BI according to what their products can do for the business enterprise
- Limited in scope; mostly refers to data analysis, querying and reporting
- Non-vendors refer to BI as a process, an organisational function, and a product
- Process – of converting data into actionable information – from unstructured data to keen insight and understanding of interrelationships of presented facts
- Organisational function – strategic management function that affects the entire or major part of organisation
- Product – processed information for the purpose of supporting business decision making